BGCSE CORE
TYPES OF NUMBERS
|
|
How is this MATHEMATICALLY correct? It seems logical. If you can figure out the ERROR in the mathematics, click here and send your reason to enter and win a free MATH TSHIRT
|
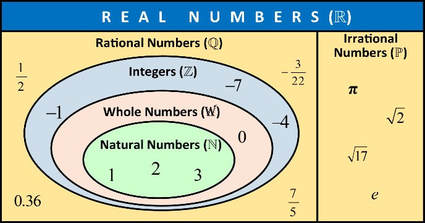
REal numbers can be classified into several categories:
|
Rational Numbers: numbers that can be written as a fraction where both the numerator and denominator are integers.
Vertical Divider
|
Irrational Numbers: numbers that CANNOT be written as fractions. For example, pi and root 2. If we try to write these numbers as decimals they go on forever, with no recurring digits.
|
|
Whole Numbers: counting numbers starting at zero. They are not negative. EXAMPLES: 0, 4, 21, 145, 2000
Natural Numbers: also called counting numbers. They are whole numbers greater than zero. They are not negative. EXAMPLES: 1, 5, 15, 215, 6204 Integers: are whole numbers, both negative and positive, including zero.EXAMPLES: -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …. Even Numbers: counting numbers that are divisible by 2. These end in 2, 4, 6, 8, 0. EXAMPLES: 256, 58, 25000, 352 Odd Numbers: counting numbers that are not divisible by 2. These end in 1, 3, 5, 7, 9. EXAMPLES: 29, 681, 4425 Vertical Divider
|
Square Numbers: integers written as the product of an integer multiplied by itself. EXAMPLES: 4 (2x2), 16 (4x4), 144 (12x12), 81 (9x9), 10000 (100x100)
Cube Numbers: integers written as the product of an integer multiplied by the square of itself. EXAMPLES: 8 (2x2x2), 27 (3x3x3), 125 (5x5x5), 1000 (10X10X10) Triangular Numbers: numbers formed by adding consecutive integers starting with 1. They form triangles when dots are used. (1, 1+2, 1+2+3…) EXAMPLES: 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 28, 36, 45, 55... Surds: Surds are numbers left in the form √n where n is a positive integer that is not a square number. Prime Numbers: numbers greater than 1 that have only two factors: 1 and the number itself. 2 is the first and only even prime number. Factors: one of two numbers, which when multiplied, give you a product. Multiples: the result of multiplying two whole numbers. |
ACTIVITIES
|
LEVEL D WORKSHEETS
Page 1 2 3 4 WORKSHEETS Types of Numbers Number Search Pascal's Triangle Triangular Numbers Squares & Square Roots Fibonacci Sequence Vertical Divider
|